Dear Editor,
Alopecia areata (AA) is an inflammatory disease of the hair follicles with a probable multifactorial origin, with autoimmune and genetic components.1 Hair loss in this condition occurs by the abrupt discontinuation of hair synthesis, without the primarily destruction of hair follicles. Therefore, AA is a potentially reversible disease. According to the main therapeutic guidelines, intralesional corticosteroids are considered first-line therapy in adults with AA involving less than 50% of the scalp.2 Intralesional infiltration of corticosteroids is considered relatively simple, effective, and minimally invasive. This route of administration transposes the epidermal barrier, delivering the drug directly into the inflamed area. Thus, it minimizes the possible adverse effects related to systemic corticosteroid therapy. In addition, penetration of the drug is more expressive compared to the topical route. The aim of this article is to suggest the use of intralesional injection of betamethasone as an alternative to triamcinolone in the treatment of alopecia areata.
Since 1956, intralesional corticosteroids have been used for the treatment of several dermatoses. Usually, triamcinolone acetonide is the most widely used injectable synthetic corticosteroid in the world, with several studies proving its efficacy.3 In Brazil, because of the lack of triamcinolone acetonide supply, the most common form of therapy is with triamcinolone hexacetonide (although there is no reference in the patient information leaflet formalizing its dermatological indication). Triamcinolone hexacetonide is found as a 20mg/mL sterile suspension and is marketed in 5mL bottles or in 1mL ampoules in packs of 5 (a single 1mL ampoule is not marketed). Dilution with saline solution, glucose, or distilled water is recommended, with an optional mixture of lidocaine. According to the leaflet, llidocaine containing methylparaben, propylparaben, or phenol should be avoided since these compounds may increase the risk of flocculation of the steroid.
A comparative study demonstrated similar efficacy of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of AA on the scalp regardless the concentration (2.5mg/mL, 5mg/mL, and 10mg/mL). However, the authors observed a lower risk of cutaneous atrophy at the lowest dose (2.5mg/mL). For the face, recommended concentrations of 2.5-5mg/mL have already been described, with a maximum concentration of 10mg/mL for the scalp, always respecting the maximum dose of 20mg per monthly session.4
A possible option for the substitution of hexacetonide is betamethasone.5 It is a low-cost, easy-to-access drug that has a formal recommendation for dermatological use in its package leaflet, which includes a specific indication for alopecia areata. In Brazil, there are two different options for betamethasone injectable suspension. The first one associates acetate salt with betamethasone disodium phosphate, both at a concentration of 3mg/mL. The second, combines dipropionate 5mg/mL with betamethasone disodium phosphate 2mg/mL. Due to the ease of access to the drug, the latter is the authors’ choice for the treatment of AA. For being more soluble, betamethasone dipropionate is rapidly absorbed. The less soluble disodium phosphate is absorbed more slowly and maintains an effective concentration of the drug for a longer time. Betamethasone is found as a sterile injectable suspension and is marketed in individual packs of 1 mL. This presentation minimizes contamination of the product as it allows for the disposal of the ampoule immediately after use.
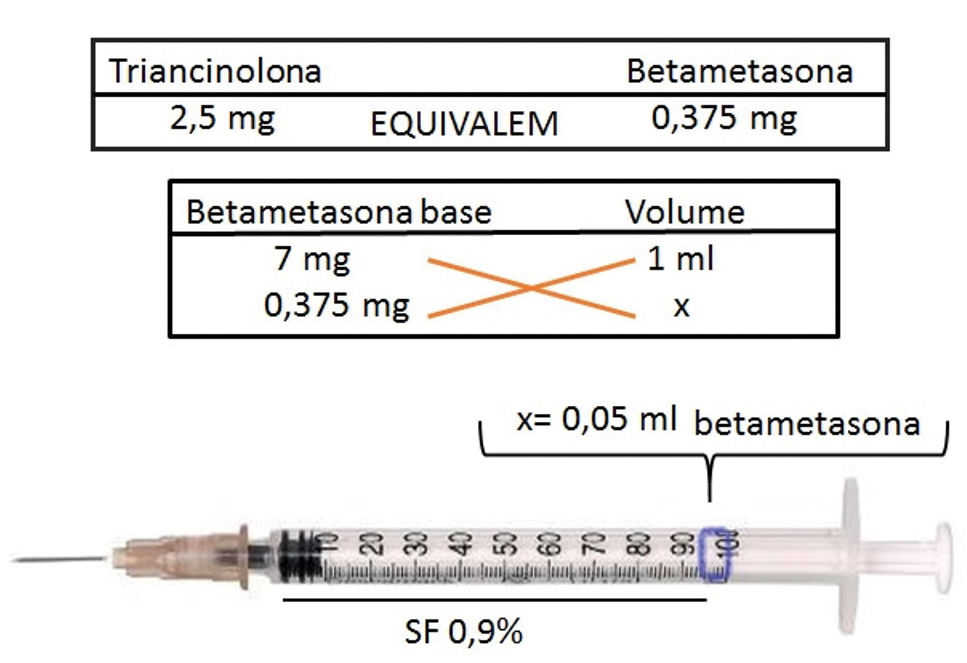
A comparative study of intralesional triamcinolone and betamethasone for the treatment of oral lichen planus demonstrated greater efficacy and less recurrence of lesions with the use of betamethasone.5 From a practical point of view, to infiltrate AA plaques using betamethasone (dipropionate 5mg/mL + disodium phosphate 2mg/mL), drug dosage should be initially calculated using the 2.5mg/mL triamcinolone concentration as a basis. This concentration is safer and as effective as higher concentrations (Figure 1).2 Using a syringe with 1 mL graduation interval and a 30G½-inch needle, aspirate 0.05mL of the medication and dilute it with a 0.9% saline solution until the syringe is full. The infiltration of 0.1mL/injection point occurs in the intradermal plane, with spacing of 0.5-1cm between the punctures and interval of 4-6 weeks between sessions.
The use of topical anesthetics, vibration, and pre-cooling of injection site may be useful to minimize procedural pain. Treatment should be discontinued if there is no improvement after six months of infiltration.2 Therefore, because it is viewed as a consecrated medication with a high anti-inflammatory potential, low cost, easy access, and with dermatological indication formalized in the package leaflet, betamethasone injectable suspension seems to be a good option to be considered as an alternative to triamcinolone in the intralesional treatment of alopecia areata.
Financial support: None.
Conflict of interests: None.