Background: Dermoscopy is a noninvasive complementary diagnostic method largely used in dermatology. Feasibility, accuracy, and reproducibility are key elements for a diagnostic method to be useful, hence the importance of the terminology used to describe dermoscopic criteria.
Objective: To evaluate the reproducibility of the English descriptive terminology proposed for dermoscopic criteria at the 3rd Consensus Meeting of the International Dermoscopy Society in Brazilian Portuguese.
Methods: Nine Brazilian dermatologists independently analyzed the translation of sixty dermoscopic descriptive terms proposed at the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Society of Dermoscopy. Interobserver agreement index was analyzed using the Fleiss’ kappa test.
Results: The interobserver agreement of the descriptive terminology in Brazilian Portuguese was considered weak (κ = 0.373; p < 0.05). The interobserver agreement of the descriptive terminology used to describe morphology and arrangement of vascular structures was considered moderate (κ = 0.43; p < 0.05).
Study limitations: Our study limitations include the small number of participants and limited regional representation (only 2 out of 5 Brazilian regions were represented).
Conclusions: The descriptive English terminology proposed at the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society revealed weak reproducibility and the morphology and arrangement of vascular structures presented moderate reproducibility in Brazilian Portuguese. Despite small regional differences, metaphoric terminology in dermoscopy seems to be the most useful and reproducible system to be adopted in Brazilian Portuguese.
Dermoscopy is a non-invasive complementary examination that allows the examiner to observe structures in cutaneous lesions not visible to the naked eye. The recognition of these structures and their histopathological correspondence is of great diagnostic assistance in dermatology. Its main application is for early diagnosis of melanoma. Provided adequate training is available, the technique can offer increased diagnostic accuracy.1 In addition to aid in diagnosing tumors, dermoscopy has been increasingly used to identify inflammatory and infectious dermatoses, alopecia, and onicopathy.
Like other methods of morphological diagnosis, its feasibility, accuracy, and reproducibility are fundamental for it to be a useful resource. Therefore, the terminology to be used in the description of its diagnostic criteria is of particular relevance. The first International Consensus Conference on dermoscopy was held in 1989 in Hamburg.2 In 1993 the adopted dermoscopic terminology was first published in Brazilian Portuguese.3 The second International Consensus Conference was held online in 2003 in order to assess intra and interobserver concordance of several dermoscopic criteria and diagnostic algorithms exclusively for dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions.4 In 2016 the third Consensus Report of the International Dermoscopy Society was published, whose objective was to establish a dictionary of standardized dermoscopic terms in English. In a survey, 1,093 professionals were asked whether they preferred metaphorical or descriptive terminology. Metaphorical language is the terminology traditionally applied that uses figurative language – such as leaf-like areas, streaks or veil – to describe structures. On the other hand, for descriptive terminology, the use of 60 terms to characterize the structures in their morphology was proposed based on five basic elements, referred to in English as lines, dots, clods, circles and pseudopods.5
The present study aimed to evaluate the reproducibility of the descriptive English terminology proposed at the third Consensus Report of the International Dermoscopy Society in Brazilian Portuguese.
MethodsNine Brazilian dermatologists from different states (Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná, Minas Gerais, and Rio Grande do Sul), with experience in dermoscopy independently evaluated the translation (suggested by the first author) into Brazilian Portuguese of the 60 descriptive and metaphorical terms proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society (Charts 1 and 2). After that, a face-to-face meeting was held to discuss the choice of the suggested Portuguese terms and their clinical significance. In cases of three or more observers, Fleiss’ kappa concordance test (κ) was used to evaluate the interobserver agreement of the descriptive Portuguese terms. According to the values obtained, agreement was considered non-existent (> 0), weak (0 - 0.39), moderate (0.4 - 0.59), good (0.60 - 0.79) or optimal (> 0.8). The test has a null hypothesis where k = 0 when there is no agreement, and k > 0 when agreement is not random. The significance level for rejection of k = 0 was set at p < 0.05.
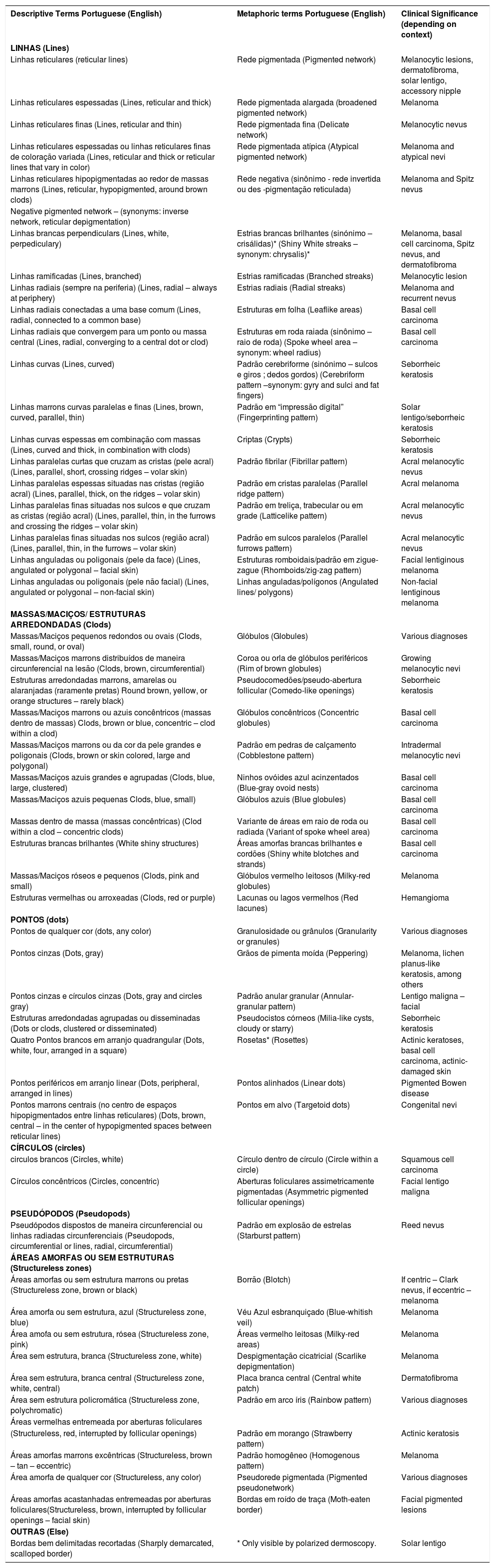
Descriptive and metaphorical dermoscopic terminology and their clinical significance as proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society and its Brazilian Portuguese equivalent
| Descriptive Terms Portuguese (English) | Metaphoric terms Portuguese (English) | Clinical Significance (depending on context) |
|---|---|---|
| LINHAS (Lines) | ||
| Linhas reticulares (reticular lines) | Rede pigmentada (Pigmented network) | Melanocytic lesions, dermatofibroma, solar lentigo, accessory nipple |
| Linhas reticulares espessadas (Lines, reticular and thick) | Rede pigmentada alargada (broadened pigmented network) | Melanoma |
| Linhas reticulares finas (Lines, reticular and thin) | Rede pigmentada fina (Delicate network) | Melanocytic nevus |
| Linhas reticulares espessadas ou linhas reticulares finas de coloração variada (Lines, reticular and thick or reticular lines that vary in color) | Rede pigmentada atípica (Atypical pigmented network) | Melanoma and atypical nevi |
| Linhas reticulares hipopigmentadas ao redor de massas marrons (Lines, reticular, hypopigmented, around brown clods) | Rede negativa (sinônimo - rede invertida ou des -pigmentação reticulada) | Melanoma and Spitz nevus |
| Negative pigmented network – (synonyms: inverse network, reticular depigmentation) | ||
| Linhas brancas perpendiculars (Lines, white, perpediculary) | Estrias brancas brilhantes (sinónimo – crisálidas)* (Shiny White streaks – synonym: chrysalis)* | Melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, Spitz nevus, and dermatofibroma |
| Linhas ramificadas (Lines, branched) | Estrias ramificadas (Branched streaks) | Melanocytic lesion |
| Linhas radiais (sempre na periferia) (Lines, radial – always at periphery) | Estrias radiais (Radial streaks) | Melanoma and recurrent nevus |
| Linhas radiais conectadas a uma base comum (Lines, radial, connected to a common base) | Estruturas em folha (Leaflike areas) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Linhas radiais que convergem para um ponto ou massa central (Lines, radial, converging to a central dot or clod) | Estruturas em roda raiada (sinônimo – raio de roda) (Spoke wheel area – synonym: wheel radius) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Linhas curvas (Lines, curved) | Padrão cerebriforme (sinónimo – sulcos e giros ; dedos gordos) (Cerebriform pattern –synonym: gyry and sulci and fat fingers) | Seborrheic keratosis |
| Linhas marrons curvas paralelas e finas (Lines, brown, curved, parallel, thin) | Padrão em “impressão digital” (Fingerprinting pattern) | Solar lentigo/seborrheic keratosis |
| Linhas curvas espessas em combinação com massas (Lines, curved and thick, in combination with clods) | Criptas (Crypts) | Seborrheic keratosis |
| Linhas paralelas curtas que cruzam as cristas (pele acral) (Lines, parallel, short, crossing ridges – volar skin) | Padrão fibrilar (Fibrillar pattern) | Acral melanocytic nevus |
| Linhas paralelas espessas situadas nas cristas (região acral) (Lines, parallel, thick, on the ridges – volar skin) | Padrão em cristas paralelas (Parallel ridge pattern) | Acral melanoma |
| Linhas paralelas finas situadas nos sulcos e que cruzam as cristas (região acral) (Lines, parallel, thin, in the furrows and crossing the ridges – volar skin) | Padrão em treliça, trabecular ou em grade (Latticelike pattern) | Acral melanocytic nevus |
| Linhas paralelas finas situadas nos sulcos (região acral) (Lines, parallel, thin, in the furrows – volar skin) | Padrão em sulcos paralelos (Parallel furrows pattern) | Acral melanocytic nevus |
| Linhas anguladas ou poligonais (pele da face) (Lines, angulated or polygonal – facial skin) | Estruturas romboidais/padrão em zigue-zague (Rhomboids/zig-zag pattern) | Facial lentiginous melanoma |
| Linhas anguladas ou poligonais (pele não facial) (Lines, angulated or polygonal – non-facial skin) | Linhas anguladas/polígonos (Angulated lines/ polygons) | Non-facial lentiginous melanoma |
| MASSAS/MACIÇOS/ ESTRUTURAS ARREDONDADAS (Clods) | ||
| Massas/Maciços pequenos redondos ou ovais (Clods, small, round, or oval) | Glóbulos (Globules) | Various diagnoses |
| Massas/Maciços marrons distribuídos de maneira circunferencial na lesão (Clods, brown, circumferential) | Coroa ou orla de glóbulos periféricos (Rim of brown globules) | Growing melanocytic nevi |
| Estruturas arredondadas marrons, amarelas ou alaranjadas (raramente pretas) Round brown, yellow, or orange structures – rarely black) | Pseudocomedões/pseudo-abertura follicular (Comedo-like openings) | Seborrheic keratosis |
| Massas/Maciços marrons ou azuis concêntricos (massas dentro de massas) Clods, brown or blue, concentric – clod within a clod) | Glóbulos concêntricos (Concentric globules) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Massas/Maciços marrons ou da cor da pele grandes e poligonais (Clods, brown or skin colored, large and polygonal) | Padrão em pedras de calçamento (Cobblestone pattern) | Intradermal melanocytic nevi |
| Massas/Maciços azuis grandes e agrupadas (Clods, blue, large, clustered) | Ninhos ovóides azul acinzentados (Blue-gray ovoid nests) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Massas/Maciços azuis pequenas Clods, blue, small) | Glóbulos azuis (Blue globules) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Massas dentro de massa (massas concêntricas) (Clod within a clod – concentric clods) | Variante de áreas em raio de roda ou radiada (Variant of spoke wheel area) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Estruturas brancas brilhantes (White shiny structures) | Áreas amorfas brancas brilhantes e cordões (Shiny white blotches and strands) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Massas/Maciços róseos e pequenos (Clods, pink and small) | Glóbulos vermelho leitosos (Milky-red globules) | Melanoma |
| Estruturas vermelhas ou arroxeadas (Clods, red or purple) | Lacunas ou lagos vermelhos (Red lacunes) | Hemangioma |
| PONTOS (dots) | ||
| Pontos de qualquer cor (dots, any color) | Granulosidade ou grânulos (Granularity or granules) | Various diagnoses |
| Pontos cinzas (Dots, gray) | Grãos de pimenta moída (Peppering) | Melanoma, lichen planus-like keratosis, among others |
| Pontos cinzas e círculos cinzas (Dots, gray and circles gray) | Padrão anular granular (Annular-granular pattern) | Lentigo maligna – facial |
| Estruturas arredondadas agrupadas ou disseminadas (Dots or clods, clustered or disseminated) | Pseudocistos córneos (Milia-like cysts, cloudy or starry) | Seborrheic keratosis |
| Quatro Pontos brancos em arranjo quadrangular (Dots, white, four, arranged in a square) | Rosetas* (Rosettes) | Actinic keratoses, basal cell carcinoma, actinic-damaged skin |
| Pontos periféricos em arranjo linear (Dots, peripheral, arranged in lines) | Pontos alinhados (Linear dots) | Pigmented Bowen disease |
| Pontos marrons centrais (no centro de espaços hipopigmentados entre linhas reticulares) (Dots, brown, central – in the center of hypopigmented spaces between reticular lines) | Pontos em alvo (Targetoid dots) | Congenital nevi |
| CÍRCULOS (circles) | ||
| circulos brancos (Circles, white) | Círculo dentro de círculo (Circle within a circle) | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| Círculos concêntricos (Circles, concentric) | Aberturas foliculares assimetricamente pigmentadas (Asymmetric pigmented follicular openings) | Facial lentigo maligna |
| PSEUDÓPODOS (Pseudopods) | ||
| Pseudópodos dispostos de maneira circunferencial ou linhas radiadas circunferenciais (Pseudopods, circumferential or lines, radial, circumferential) | Padrão em explosão de estrelas (Starburst pattern) | Reed nevus |
| ÁREAS AMORFAS OU SEM ESTRUTURAS (Structureless zones) | ||
| Áreas amorfas ou sem estrutura marrons ou pretas (Structureless zone, brown or black) | Borrão (Blotch) | If centric – Clark nevus, if eccentric – melanoma |
| Área amorfa ou sem estrutura, azul (Structureless zone, blue) | Véu Azul esbranquiçado (Blue-whitish veil) | Melanoma |
| Área amofa ou sem estrutura, rósea (Structureless zone, pink) | Áreas vermelho leitosas (Milky-red areas) | Melanoma |
| Área sem estrutura, branca (Structureless zone, white) | Despigmentação cicatricial (Scarlike depigmentation) | Melanoma |
| Área sem estrutura, branca central (Structureless zone, white, central) | Placa branca central (Central white patch) | Dermatofibroma |
| Área sem estrutura policromática (Structureless zone, polychromatic) | Padrão em arco íris (Rainbow pattern) | Various diagnoses |
| Áreas vermelhas entremeada por aberturas foliculares | ||
| (Structureless, red, interrupted by follicular openings) | Padrão em morango (Strawberry pattern) | Actinic keratosis |
| Áreas amorfas marrons excêntricas (Structureless, brown – tan – eccentric) | Padrão homogêneo (Homogenous pattern) | Melanoma |
| Área amorfa de qualquer cor (Structureless, any color) | Pseudorede pigmentada (Pigmented pseudonetwork) | Various diagnoses |
| Áreas amorfas acastanhadas entremeadas por aberturas foliculares(Structureless, brown, interrupted by follicular openings – facial skin) | Bordas em roído de traça (Moth-eaten border) | Facial pigmented lesions |
| OUTRAS (Else) | ||
| Bordas bem delimitadas recortadas (Sharply demarcated, scalloped border) | * Only visible by polarized dermoscopy. | Solar lentigo |
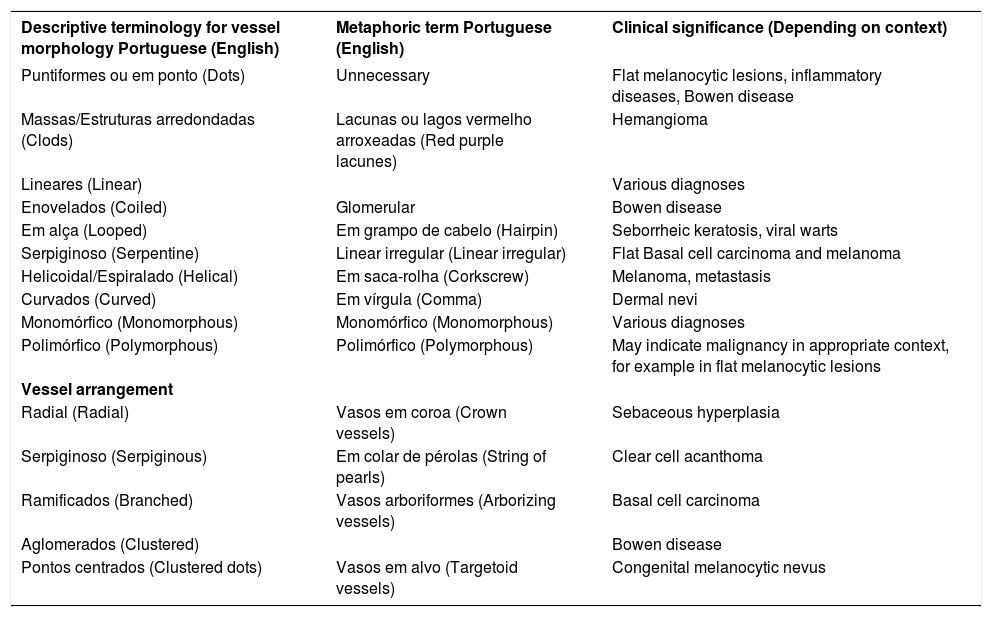
Descriptive and metaphorical dermoscopic terminology and its clinical significance concerning vessel morphology and arrangement as proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society and its Brazilian Portuguese equivalent
| Descriptive terminology for vessel morphology Portuguese (English) | Metaphoric term Portuguese (English) | Clinical significance (Depending on context) |
|---|---|---|
| Puntiformes ou em ponto (Dots) | Unnecessary | Flat melanocytic lesions, inflammatory diseases, Bowen disease |
| Massas/Estruturas arredondadas (Clods) | Lacunas ou lagos vermelho arroxeadas (Red purple lacunes) | Hemangioma |
| Lineares (Linear) | Various diagnoses | |
| Enovelados (Coiled) | Glomerular | Bowen disease |
| Em alça (Looped) | Em grampo de cabelo (Hairpin) | Seborrheic keratosis, viral warts |
| Serpiginoso (Serpentine) | Linear irregular (Linear irregular) | Flat Basal cell carcinoma and melanoma |
| Helicoidal/Espiralado (Helical) | Em saca-rolha (Corkscrew) | Melanoma, metastasis |
| Curvados (Curved) | Em vírgula (Comma) | Dermal nevi |
| Monomórfico (Monomorphous) | Monomórfico (Monomorphous) | Various diagnoses |
| Polimórfico (Polymorphous) | Polimórfico (Polymorphous) | May indicate malignancy in appropriate context, for example in flat melanocytic lesions |
| Vessel arrangement | ||
| Radial (Radial) | Vasos em coroa (Crown vessels) | Sebaceous hyperplasia |
| Serpiginoso (Serpiginous) | Em colar de pérolas (String of pearls) | Clear cell acanthoma |
| Ramificados (Branched) | Vasos arboriformes (Arborizing vessels) | Basal cell carcinoma |
| Aglomerados (Clustered) | Bowen disease | |
| Pontos centrados (Clustered dots) | Vasos em alvo (Targetoid vessels) | Congenital melanocytic nevus |
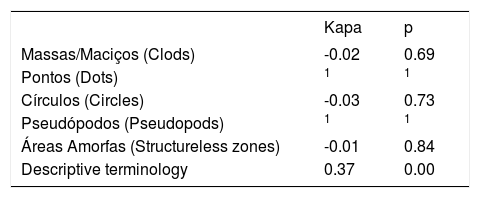
Interobserver agreement was considered weak (κ = 0.373, p < 0.05) regarding the acceptance of the descriptive terminology in Brazilian Portuguese. Additionally, a lack of concordance with terms related to clods criterion (κ = -0.02) and circles criterion (κ = -0.03) (Table 1) was observed.
Interobserver agreement of the Brazilian Portuguese translation of the terminology as proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society
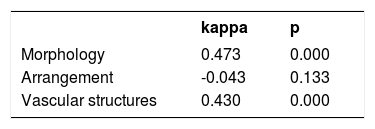
In relation to the descriptive terminology used for the morphology and arrangement of vascular structures, the interobserver concordance was considered moderate (κ = 0.43, p < 0.05) (Table 2).
Interobserver agreement of the Brazilian Portuguese terminology used to describe morphology and arrangement of vascular structures as proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society
| kappa | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Morphology | 0.473 | 0.000 |
| Arrangement | -0.043 | 0.133 |
| Vascular structures | 0.430 | 0.000 |
(*) There was no inter-observer discordance; k is not applicable.
The descriptive terminology adopted by the English authors is based on five elements: lines, dots, clods, circles, and pseudopods. Paradoxically, two of these terms are metaphorical – clods and pseudopods – which makes the comparison between metaphorical and descriptive terminology incoherent. A metaphor, by definition, is a semantic resource for improving the expressiveness of what one wishes to express. Although most authors are quite familiar with metaphorical terms in dermoscopic terminology, one must be receptive to this new descriptive strategy should they become part of the professional environment. However, in our professional opinion, the five basic terms adopted in English are not adequate to be included in the Brazilian Portuguese terminology since their reproducibility was considered weak (κ = 0.373 p < 0.05).6
The typical appearance of a pigmented network is related both to its color and to the thickness of its lines. The distinction between broadened network and atypical network lies in the fact that atypical networks display an increased variability in color, with no thickness variation, whereas the broadened network, as the term suggests, displays a widening of the network lines. Both atypical and broadened networks are not unique to melanoma and can often be found in atypical melanocytic nevi. We observed a subtle variation of the terminology in Portuguese since three evaluators use the term rede pigmentar instead of rede pigmentada to refer to a pigmented network. Although inverse pigmented network is more frequently observed in melanoma and Spitz nevus, it can also be found in atypical and congenital nevi.
The fingerprint pattern is characteristic of solar lentigo. However, it can also be observed in seborrheic keratoses.
Maple leaflike structures, classically described in basal cell carcinoma, correspond to the intradermal masses of basaloid cells and do not display a linear aspect. They should not, therefore, be classified from the descriptive point of view as lines, but rather as masses or clods.
According to Japanese authors, the parallel ridge pattern is most frequently found in melanomas (99% in their series).7 According to the proposed algorithm, all plantar lesions exhibiting a parallel ridge pattern should be biopsied.8 Some exceptions are known such as paint pigmentation, Peutz-Jeughers syndrome, acral pigmentation due to the use of anticancer drugs, and pigmented plantar warts.8 Particularly in our milieu, racial melanosis is very frequent and may also exhibit a parallel ridge pattern.9,10
The literal translation of the English term “clod” – adopted by the consensus conference as being a descriptive term – would not make sense in Brazilian Portuguese. In our study, we suggested the terms massas, maciços, estruturas, aglomerados, and glóbulos (masses, lumps, structures, agglomerates, and globules, respectively). Therefore, the precise descriptive terms are not the best option to be included by in the Portuguese dermoscopic terminology. Thus, the metaphorical terms are more reproducible for this type of structure.
Although “gray dots” or “peppering” can be found in melanoma and benign lichenoid keratoses, they can also be observed in any condition with liquefaction of the basal layer and leakage in the dermis of melanin pigment.
The annular-granular pattern, despite being characteristic of lentiginous melanoma in situ, can also be identified in facial seborrheic and actinic keratoses.
Pseudopods found circumferentially in the classic “starburst” pattern of Reed nevus may be occasionally observed irregularly and asymmetrically in melanomas.
Centralized blotches (fried egg appearance) suggest dysplastic melanocytic nevi, and peripheral blotches suggest melanomas. In melanodermic patients, however, blotches can be observed in common melanocytic nevi at the center of the lesion.
Scarlike depigmentation may occasionally be observed in melanoma in areas where the controversial regression phenomenon is observed. However, this sign is not pathognomonic since it may also occur in areas of melanocytic or non-melanocytic traumatic lesions. Other names for this metaphorical term suggested by the authors were áreas de regressão, hipopigmentação tipo pseudocicatriz, and fibrose (regression zones, pseudo scar-like hypopigmentation, and fibrosis, respectively).
The structureless polychromatic zone, also referred to as a “rainbow pattern”, can be identified in several entities, but it is more significant in the diagnosis of Kaposi’s sarcoma.
The interobserver agreement with the descriptive terminology in Portuguese, when the vascular criteria were considered, was higher than when compared to the other criteria. In our study, it was classified as moderate (κ = 0.43; p < 0.05). “Looped” or “hairpin” vessels, in addition to being found in seborrheic keratoses and viral warts, may also be observed in keratoacanthomas and intradermal melanocytic nevi. When surrounded by a clear halo, they suggest the keratinocyte lineage of the tumor. Spiral or “corkscrew” helical vessels can also be found in cutaneous metastases of non-melanoma tumors.
Differently from the lack of consensus observed in the English language regarding the terms dermoscopy and dermatoscopy, in our environment there seems to be no disagreement as to the predilection of the well-established Portuguese term dermatoscopia, and not dermoscopia.5
ConclusionThe descriptive English terminology proposed by the 3rd Consensus Conference of the International Dermoscopy Society revealed weak reproducibility in Brazilian Portuguese and the descriptive dermatoscopic terminology related to morphology and arrangement of vascular structures showed moderate reproducibility. Despite small regional differences, metaphorical dermoscopic terminology seems to be the most useful and reproducible system to be adopted in Brazil.