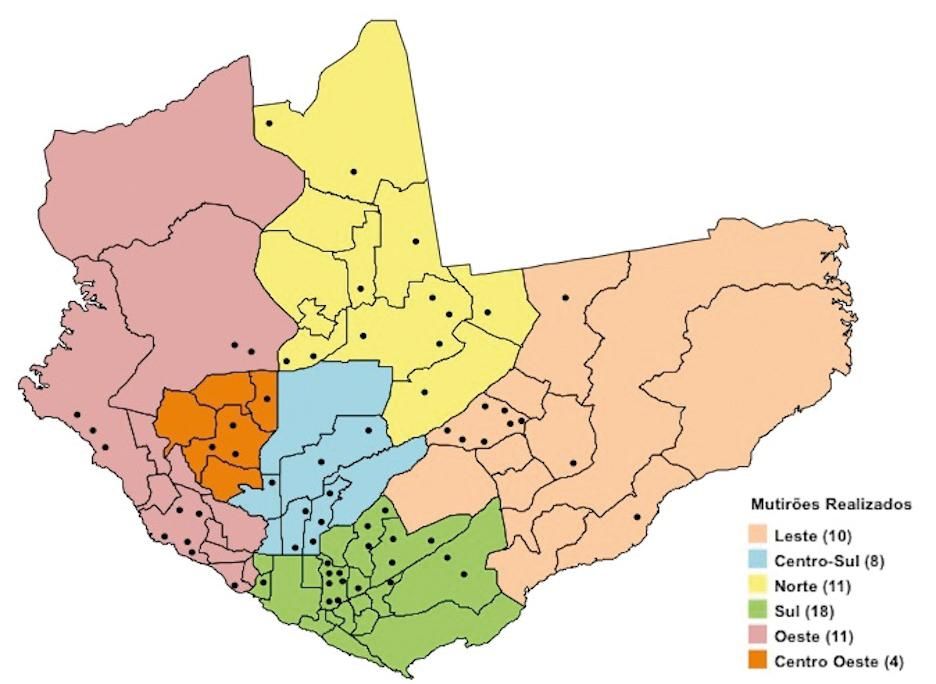
Brazil together with India are the countries that have the highest rates of endemicity of leprosy in the world.1 Among the measures to reduce these levels and the stigma that accompanies the disease for centuries, due to the incapacities that it can lead to, are early diagnosis and immediate polychemotherapeutic treatment against Mycobacterium leprae for the breakdown of the transmission chain.2 Amazonas, a state with a high level of leprosy, was a pioneer in the implementation of multidrug therapy in Brazil in the early 1980s, which, along with other routine control activities such as training and supervision of health teams, examination of intradomiciliary contacts of new cases and active search in school students and in communities, has led to a consistent fall in the disease detection coefficient over the years, from 75.5 in 1990 to 11.07 in 2016.3 However, it is a State that has the uniqueness of a reference center (Alfredo da Matta Foundation) being in charge of the Leprosy Control Program since its inception, with the deactivation of the isolation colony, which facilitates the execution of control activities by having a specialized and engaged team. Among these activities, the active search for cases in the communities is a priority strategy and, in recent years, has been done systematically, monthly, on a Saturday morning in the physical space of a school or health service, with the so-called dermatological care units, with a multidisciplinary team.4,5 Thus, in the years 2015 to 2017, there were 62 joint efforts in the city of Manaus, the state capital, with 2,130,264 inhabitants, covering the six districts of the city (Figure 1), with a total of 12,617 leading to the diagnosis of 112 confirmed cases of leprosy, 40 (35.7%) paucibacillary and 72 (64.3%) multibacillary representing 19.2% of the 582 new cases of leprosy detected and reported in Manaus, during the same period. This result points to the importance of the active search for cases in the diagnosis of leprosy as a strategy to reach a repressed demand, either by the difficulty of access or by the provision of health services.
Financial support: None.
Conflict of interest: None.