Benign migratory glossitis or geographic tongue is a benign condition that usually manifests as asymptomatic erythematous and migratory circinate patches, involving the lateral and dorsal aspects of the tongue. Extra-lingual lesions uncommonly occur and are mainly located on labial and buccal mucosae, lips and floor of the mouth. The present report describes one patient with a geographic lesion on the hard palate associated with lingual lesions and another patient who had multiple geographic lesions both in the hard and soft palate without lingual lesions. We found 64 cases in the English literature of ectopic locations with 22 palate involvement. No case of simultaneous involvement of the hard and the soft palate was found.
Benign migratory glossitis or geographic tongue (GT) is a benign condition which usually manifests as asymptomatic erythematous and migratory circinate patches, involving the lateral and dorsal aspects of the tongue.1 Extra-lingual lesions (i.e. geographic stomatitis) uncommonly occur and are mainly located on labial and buccal mucosae, lips and floor of the mouth.1,2 We report two cases of ectopic GT with an unusual involvement of the palate.
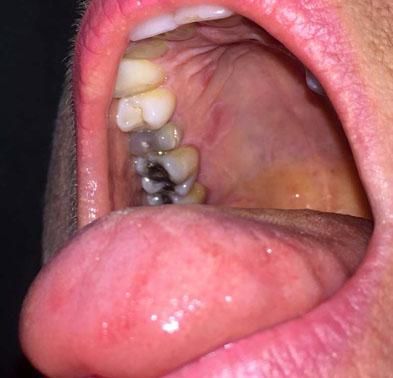
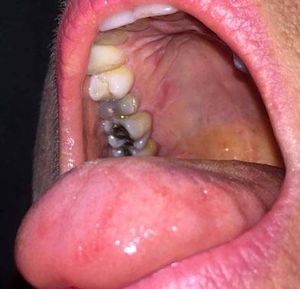
Case ReportsCase 1A 53-year-old Caucasian woman was referred for the recent development of an asymptomatic lesion of the hard palate (Figure 1). Her medical history included a caesarean section and a uterine fibroid. She was not taking any medication. Oral examination revealed a circumscribed red lesion, surrounded by a white circular border on the right part of the hard palate. Concomitant erythematous patches on the dorsal aspect of the tongue, with loss of filiform papillae, were noted. These asymptomatic lingual lesions evolved with periods of exacerbation and remission and were very suggestive of GT. Extra-oral lesions were not observed. The diagnosis of GT with an ectopic palate lesion was made. The patient was reviewed 2 weeks later, and the palatal lesion had disappeared.
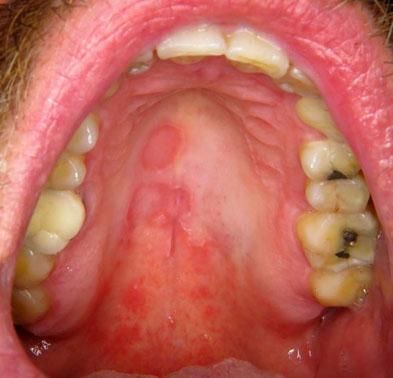
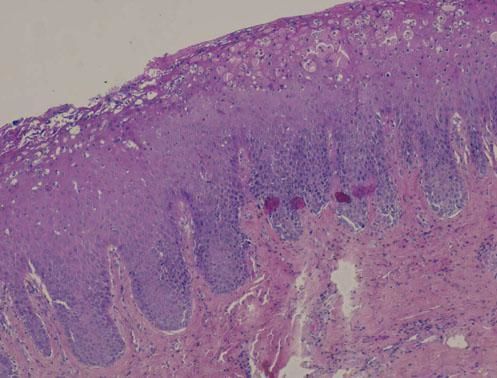
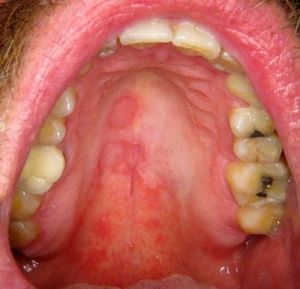
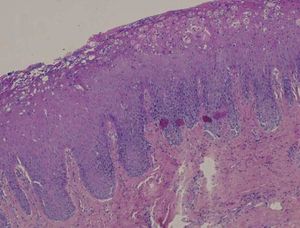
Case 2A 47-year-old Caucasian man presented with symptomatic erythematous lesions involving both the hard and the soft palate. He had a medical history of rheumatoid purpura, bilharziasis, asthma and treated arterial hypertension. The patient was taking nicardipine and a combination of formoterol and beclomethasone in spray form. Extra-oral lesions were not observed. Five days later, a raised yellowish circle surrounding the red patches was noted, suggesting geographic stomatitis with palate involvement (Figure 2). Histopathological findings showed a hyperplastic and budding mucosa with no associated hyperkeratosis, together with elongation of rete ridges (Figure 3). The mucosa was eroded, with a focal infiltrate of neutrophils. A mild sub-epithelial inflammatory reaction was associated. Direct immunofluorescence was negative. The diagnosis of geographic stomatitis with palate involvement was made.
Benign migratory glossitis or GT, first described by Rayer in 1831, is a common condition usually occurring in childhood, with a global prevalence which varies between 0.5 and 1.5%.3 In 1982, Hume proposed a clinical classification according to the aspect of lesions and their anatomical localizations:1
- •
Type 1 is the classic form with an exclusively lingual involvement and characteristic circinate migratory lesions.
- •
Type 2 corresponds to the association of lesions of type 1 with lesions elsewhere in the mouth.
- •
Type 3 is observed with non-characteristic lingual lesions, which may or may not be accompanied by other oral lesions. A fixed form (non-migrating and recurrent lesions in the same place) and an abortive form (lesion starting with a white patch and disappearing before achieving the typical appearance of GT) can be distinguished.
- •
Type 4 which is also called geographic stomatitis (or migratory stomatitis), corresponds to lesions elsewhere in the mouth without the presence of GT.
According to this classification, our patients respectively presented a type 2 and a type 4 GT.
GT exhibits a slight female predominance,1,2 but van der Wall et al.1 showed a male predominance in ectopic locations. The classic appearance of geographic lesions is characterized by one or more erythematous patches surrounded by a raised white border.1–3 Lesions disappear spontaneously and reappear in another location, sometimes within a few hours.3 The main location is the dorsum or the lateral borders of the tongue. Ectopic locations were rarely reported, mainly in the buccal and lower labial mucosa, as well as on the ventral side of the tongue.1–4
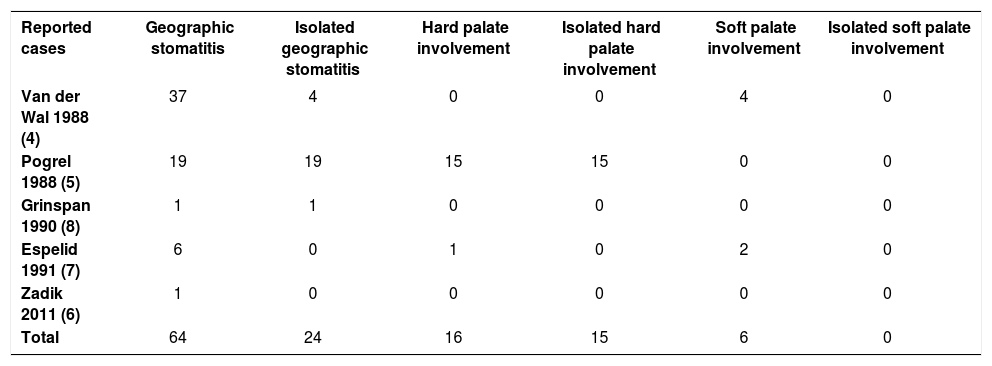
In the English literature, we isolated 64 cases of ectopic lesions (Table 1).4,5–8 Among them, only 24 developed in isolation.4,5,8 Twenty-two ectopic lesions affected the palate, mainly the hard palate.5,7 Hard palate involvement occurred almost exclusively in isolation and was always associated with skin psoriasis.5,7 By contrast, lesions of the soft palate are never isolated. Simultaneous involvement of the hard and the soft palate was not found in this review.4,7
Review of reported cases of geographic stomatitis
| Reported cases | Geographic stomatitis | Isolated geographic stomatitis | Hard palate involvement | Isolated hard palate involvement | Soft palate involvement | Isolated soft palate involvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Van der Wal 1988 (4) | 37 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Pogrel 1988 (5) | 19 | 19 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Grinspan 1990 (8) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Espelid 1991 (7) | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Zadik 2011 (6) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 64 | 24 | 16 | 15 | 6 | 0 |
Diagnosis of GT is clinical, but histology may be useful for atypical or ectopic forms.1,2,4,9 No histological differences between ectopic localizations and GT have been noted.4 The white area of lesion presents parakeratosis, epithelial acanthosis associated with an elongation of the rete ridges, an infiltrate of neutrophils forming Munro’s microabscesses, as well as ruptured interkeratinocytic junctions.1,2,9 The histopathological aspects of the erythematous area includes a subepithelial infiltrate of mononuclear cells (predominantly CD4+ T-lymphocytes), associated with a disappearance of the filiform papillae and the granular layer, as well as an incomplete keratinization.2,3,9 This aspect is very suggestive of psoriatic disease.2,3,4,9
The etiology remains unknown.1,2 Familial forms are described and support the existence of hereditary factors.3 Associations with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, HIV, atopic dermatitis and Reiter syndrome have been reported.4,9 Recently, GT has been described in association with targeted anticancer therapies that inhibit the vascular endothelial growth factor or its receptors. However, the most prevalent association is with psoriasis. Several studies found a significantly increased incidence of GT and fissured tongue (FT) in psoriatic patients compared with control groups.9,10 According to some authors, FT corresponds to an advanced stage of GT, and the two conditions are associated in 50% of cases.1,3,4,9 In a recent literature review, Picciani et al.9 found immunogenetic similarities between GT and psoriasis, in particular a common genetic marker: HLA-C*06. So, clinical association, histological similarities and a genetic link suggest that GT is an oral manifestation of psoriasis even in the absence of other signs of the disease.2,9,10
Geographic lesions do not require any treatment -- except to reassure the patient -- when they are asymptomatic.2,3 Several topical treatments have been proposed for painful lesions, e.g. corticosteroids, vitamin A, antihistamines, anesthetics or tacrolimus.2,9
Geographic tongue is a common condition, but ectopic locations are probably underdiagnosed. Palate involvement is exceptional in this context. Diagnosis can be challenging, especially in the absence of an association with more characteristic lingual involvement. □