Dear Editor,
Contact dermatitis (CD) is one of the most common diseases seen in dermatological practice. It represents the majority of occupational dermatoses and produces a considerable socioeconomic impact, especially in industrialized countries.1 CD is caused by external agents that trigger inflammatory reactions through multiple mechanisms when they come into contact with the skin. Patch tests are considered the gold-standard complementary exam for the diagnosis of CD.
Data from the literature suggest that 1-5.4% of the population is sensitized to some cosmetic substance, with about 80% of cases occurring among female patients aged between 20 and 60 years.2 Despite the growing number of cases of CD, Brazilian etiological and epidemiological data are scarce.
The present study - approved by the Ethics Committee of The Federal University of Health Sciences of Porto Alegre (Porto Alegre - RS, Brazil) - evaluated a prospective sample of patients that attended the Dermatology Service at that University aiming to determine the prevalence of allergic CD due to cosmetics and, thus, reveal its etiological profile and associated factors. This cross-sectional study included 28 patients with suspected cosmetic-induced CD (January-October 2016) that agreed with the terms and conditions of the study. Three batteries approved by the Brazilian Society of Dermatology were applied: the Brazilian standard battery, the cosmetic battery, and the hair cosmetic battery (IPI ASACPHARMA®). The results were analyzed according to the criteria of the International Dermatitis Research Group.
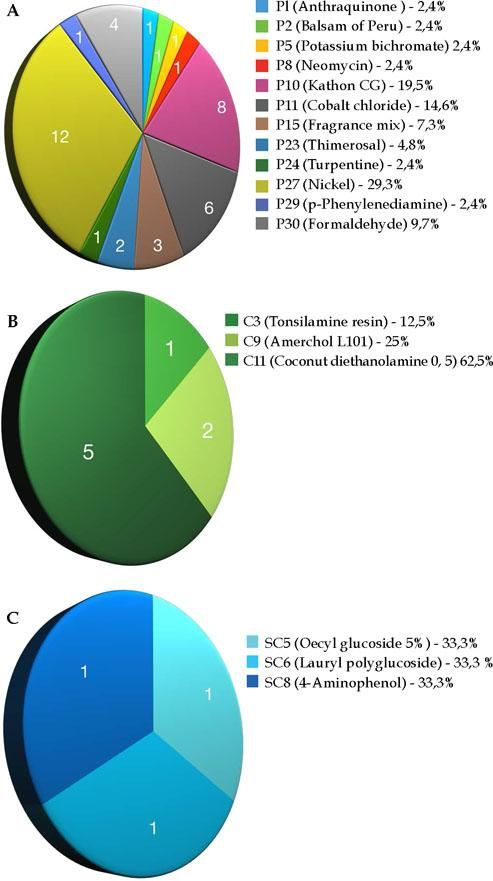
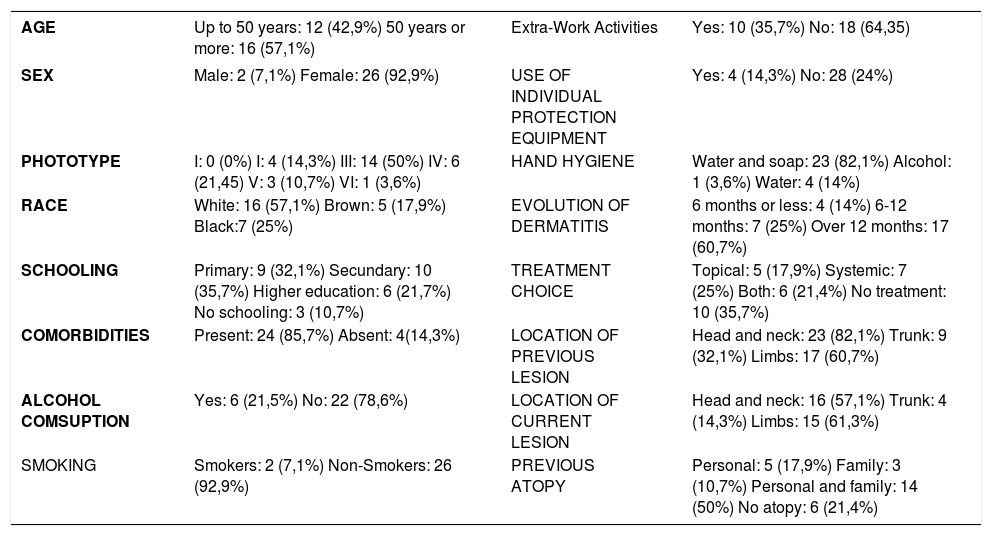
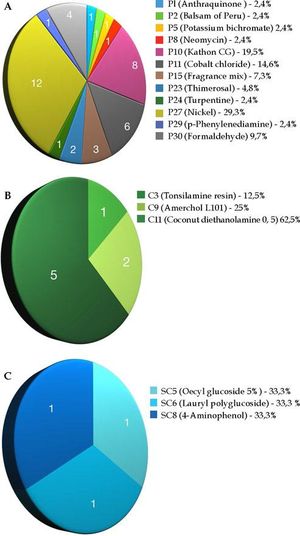
The statistical analysis of the data was performed using the SPSS-23 software; chi-squared tests with a significance level of 95% (p < 0.05) were used. Females predominated (92.9%) and the median age was 51 years; 43% tested positive for the standard battery, 29% for the cosmetic battery and 11% for the hair cosmetic battery, where nickel (29%), coconut diethanolamine (63%), and decyl glucoside (34%) were, respectively, the most frequent agents in each battery. A total of 89.3% of the tests were considered relevant and the lesions were most frequently located on the head and neck (57.1%). Clinical improvement within 30 days of the removal of allergens was reported by 92.9% of the patients. Angry back syndrome was observed in three patients (10.7%) and patients over 50 years of age were positive in 59.1% of the tests. No significant association was found between history of atopy and testing positive (p <0,610).
Table 1 and graph 1 present the data from the present research and compares them with those found in the literature, thus the following considerations can be made: previous studies found the face to be the region most frequently affected by cosmetic-induced CD, while the present study found a greater frequency in the head and neck. The components of fragrances and preservatives are the most frequent contact cosmetic allergens.3
General characterization of subjects
| AGE | Up to 50 years: 12 (42,9%) 50 years or more: 16 (57,1%) | Extra-Work Activities | Yes: 10 (35,7%) No: 18 (64,35) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEX | Male: 2 (7,1%) Female: 26 (92,9%) | USE OF INDIVIDUAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT | Yes: 4 (14,3%) No: 28 (24%) |
| PHOTOTYPE | I: 0 (0%) I: 4 (14,3%) III: 14 (50%) IV: 6 (21,45) V: 3 (10,7%) VI: 1 (3,6%) | HAND HYGIENE | Water and soap: 23 (82,1%) Alcohol: 1 (3,6%) Water: 4 (14%) |
| RACE | White: 16 (57,1%) Brown: 5 (17,9%) Black:7 (25%) | EVOLUTION OF DERMATITIS | 6 months or less: 4 (14%) 6-12 months: 7 (25%) Over 12 months: 17 (60,7%) |
| SCHOOLING | Primary: 9 (32,1%) Secundary: 10 (35,7%) Higher education: 6 (21,7%) No schooling: 3 (10,7%) | TREATMENT CHOICE | Topical: 5 (17,9%) Systemic: 7 (25%) Both: 6 (21,4%) No treatment: 10 (35,7%) |
| COMORBIDITIES | Present: 24 (85,7%) Absent: 4(14,3%) | LOCATION OF PREVIOUS LESION | Head and neck: 23 (82,1%) Trunk: 9 (32,1%) Limbs: 17 (60,7%) |
| ALCOHOL COMSUPTION | Yes: 6 (21,5%) No: 22 (78,6%) | LOCATION OF CURRENT LESION | Head and neck: 16 (57,1%) Trunk: 4 (14,3%) Limbs: 15 (61,3%) |
| SMOKING | Smokers: 2 (7,1%) Non-Smokers: 26 (92,9%) | PREVIOUS ATOPY | Personal: 5 (17,9%) Family: 3 (10,7%) Personal and family: 14 (50%) No atopy: 6 (21,4%) |
While in the United Kingdom 23% of women and 18,8% of men experienced adverse reactions to a personal care product; in this study, considering all allergens tested, 13 (46%) patients effectively experienced an allergic reaction to some cosmetic component and 11 (39%) had a positive reaction to more than one agent in all three batteries. 4
The most common allergens were nickel, kathon (methylisothiazoline), and cobalt in the standard battery; coconut diethanolamine, amerchol L101, and tosilamide resin in the cosmetic battery; and decylglucoside 5%, lauryl polyglucose, and P-aminophenol in the hair cosmetic battery. An earlier study showed that nickel presented a higher prevalence of sensitization when isolated than other metals and was the main sensitizer in women.3
Kathon, which is used as a cosmetic marker, is considered one of the major clinical causes of allergic dermatitis. A study carried out in São Paulo, Brazil, found that 46% of tests were positive for cosmetics and the main causative agents were butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and triethanolamine (causing 19,18% of cases each), followed by ammonium thioglycolate (17,81%), sorbic acid (12,33%), tosylamide (10,95%), and germall (8,22%). 5 In the hair cosmetic battery, we found a lower prevalence of allergies but there are no studies to establish a comparison.
More studies focusing on the prevalence of CD to cosmetics (including its components) in different regions of Brazil are necessary given their frequent use. Multicentric studies with standardized methodologies and larger patient samples should be encouraged so that the main sensitizing agents and their allergenic potential can be identified and reported. □
AcknowledgementsWe would like to thank all patients that participated in the study, the IPI ASACPHARMA company for donating the contact test batteries, and to the UFCSPA Dermatology Service (resident medical colleagues, academics, preceptors and employees).